Hash模式和History模式的區別
不管哪種模式�����,前端路由都是客戶端路由的實現方式�,也就是當路徑發生變化時���,不會向服務器發送請求,是利用js監視路徑的變化���。然后根據不同的地址渲染不同的內容���,如果需要服務器內容�,會發送Ajax請求來獲取����。
表現形式的區別
-
hash 模式
https://music.163.com/#/discover/toplist 地址中會存在 # 號
-
history 模式
https://music.163.com/discover/toplist 地址中沒有# 類似于普通的地址,但是需要服務端配置支持
原理的區別
-
hash 模式是基于錨點�, 以及onhashchange 事件
-
history 模式是基于 HTML5 中的 History API
-
history.pushState() IE10 以后才支持
-
history.replaceState() \
History 模式的使用
-
History 需要服務器的支持
-
單頁應用中,如果刷新頁面����,會向服務器發起請求,而服務器不存在這樣的地址就會返回找不到該頁面從而出現404
-
在服務端應該除了靜態資源外都返回單頁應用的 index.html
node 環境下支持 history
在 node 環境下���,啟用對history模式的支持可以通過 connect-history-api-fallback 這個中間件來完成
const history = require('connect-history-api-fallback') const express = require('express') const app = express() app.use(history())
Nginx 下支持 history
-
從官網下載 nginx 的壓縮包
-
把壓縮包解壓到 c 盤根目錄�����,c:\nginx-1.18.0 文件夾
-
修改 conf\nginx.conf 文件
運行nginx服務器基本指令
啟動
start nginx
重啟
nginx -s reload
停止
nginx -s stop
location / { root html; index index.html index.htm; #新添加內容
#嘗試讀取$uri(當前請求的路徑)���,如果讀取不到讀取$uri/這個文件夾下的首頁
#如果都獲取不到返回根目錄中的 index.html
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html; }
VueRouter 兩種模式的實現原理
Hash 模式
-
URL 中 # 后面的內容作為路徑地址
-
監聽 hashchange 事件
-
根據當前路由地址找到對應組件重新渲染
History 模式
-
通過 history.pushState() 方法改變地址欄
-
監聽 popstate 事件
-
根據當前路由地址找到對應組件重新渲染
實現思路
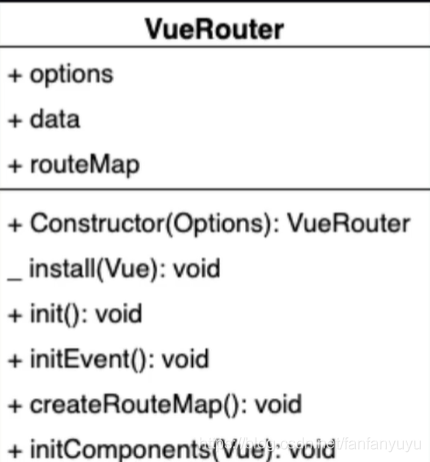
從上圖,可以大致了解一下 VueRouter 這個類中的結構:
上半部分是屬性,下半部分是方法��,其中+ 是實例方法���,- 是靜態方法�����。
install 是用來實現Vue.use 插件機制的方法�。
VueRouter-install 方法實現
要實現install方法�,首先先分析一下該方法要做的事情:
-
判斷當前插件是否已經被安裝
-
把Vue構造函數記錄到全局變量
-
把創建Vue實例時候傳入的router對象注入到所有的Vue實例上
let _Vue; export default class VueRouter { static install(Vue) { if(VueRouter.install.installed) return VueRouter.install.installed = true _Vue = Vue _Vue.mixin({ beforeCreate(){ if(this.$options.router) { _Vue.prototype.$router = this.$options.router } } }) } }
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
-
5
-
6
-
7
-
8
-
9
-
10
-
11
-
12
-
13
-
14
-
15
-
16
-
17
-
18
-
19
-
20
-
21
-
22
-
23
添加 VueRouter 的constructor
VueRouter 的構造函數要初始化三個屬性���,分別是: options��、data��、routeMap�����。
-
options 是路由的構造配置對象
-
data 應該是一個響應式的對象��,其中有一個屬性 current 用來記錄當前我們的路由地址��,這里我們該如何才能創建一個響應式的對象呢?可以使用Vue的observable方法
-
routeMap 中記錄了 options里的rules�,rules解析出來 會以鍵值對的形式存在 routeMap中 �����,key 就是路由地址�����,value 就是路由組件
constructor(options){ this.options = options this.data = _Vue.observable({ current:'/' }) this.routeMap = {} }
createRouterMap
接下來我們來實現VueRouter類中 createRouterMap 這個方法���,它的作用就是把 options 中rules 路由規則解析出來以鍵值對的形式存儲在routeMap上���。
createRouterMap() { this.options.rules.forEach(route => this.routeMap[route.path] = route.component) }
initComponents
下一步,來創建initComponents 方法�,這個方法里我們要創建兩個組件。分別是:RouterLink 和 RouterView
創建RouterLink 組件
let _Vue; export default class VueRouter { static install(Vue) { if (VueRouter.install.installed) return VueRouter.install.installed = true _Vue = Vue _Vue.mixin({ beforeCreate() { if (this.$options.router) { _Vue.prototype.$router = this.$options.router this.$options.router.init() } } }) } constructor(options) { this.options = options this.routeMap = {} this.data = _Vue.observable({ current: '/' }) } createRouterMap() { this.options.routes.forEach(route => this.routeMap[route.path] = route.component) } initComponents(Vue) { Vue.component('router-link', { props: { 'to': { type: String } }, template: `<a :href="to"><slot></slot></a>` }) } init() { this.createRouterMap() this.initComponents(_Vue) } }
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
-
5
-
6
-
7
-
8
-
9
-
10
-
11
-
12
-
13
-
14
-
15
-
16
-
17
-
18
-
19
-
20
-
21
-
22
-
23
-
24
-
25
-
26
-
27
-
28
-
29
-
30
-
31
-
32
-
33
-
34
-
35
-
36
-
37
-
38
-
39
-
40
-
41
-
42
-
43
-
44
-
45
-
46
用自己的VueRouter 替換掉官方的運行后�,發現報錯
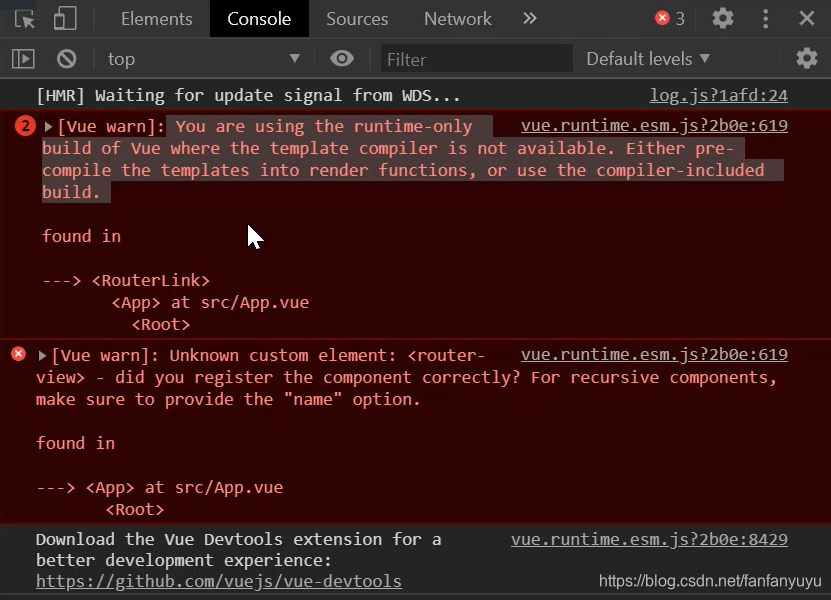
報錯的意思是,運行時版本的Vue 不支持 tempalte 模板��,需要打包的時候提前編譯�。
如果要讓我們的template被支持可以使用完整版的Vue,完整包包含運行時和編譯器�,體積比運行時版本大10k左右����,程序運行的時候把模板轉換成render函數
@vue/cli 自動安裝的就是 運行時版本
報錯的解決
第一種方案——引入完整版Vue����,可以在vue.config.js中 加入配置
module.exports = { runtimeCompiler: true }
第二種方案——使用render函數替換掉tempalte
render(h) { return h('a', { attrs: { href: this.to } }, [this.$slots.default]) }
創建RouterView組件
let self = this Vue.component('router-view',{ render(h){ return h(self.routeMap[self.data.current]) } })
在routerlink中添加點擊事件,修改地址
為了能夠讓鏈接成功完成跳轉展示組件���,我們需要對routerlink中的a標簽添加點擊事件
并且要在點擊的時候�,把最新的path更新到router實例的current上.
我們借助于history的pushState方法 該方法會修改瀏覽器地址欄中的地址����,但不會向服務器發起請求,并且還可以將新地址記錄在歷史中
Vue.component('router-link', { props: { 'to': { type: String } }, render(h) { return h('a', { attrs: { href: this.to }, on: { click: this.clickHandle } }, [this.$slots.default]) }, methods: { clickHandle(e) { history.pushState({}, "", this.to) this.$router.data.current = this.to
e.preventDefault() } } })
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
-
5
-
6
-
7
-
8
-
9
-
10
-
11
-
12
-
13
-
14
-
15
-
16
-
17
-
18
-
19
-
20
initEvent
現在功能基本上已經差不多了��,但是還存在一個小問題�����,就是當我們點擊瀏覽器的前進或者后退按鈕的時候����,組件不能實現切換展示,主要思路就是通過添加popstate監聽地址變化���,下面我們來完善該功能
initEvent(){ window.addEventListener("popstate",()=>{ this.data.current = window.location.pathname }) }
完整代碼
let _Vue; export default class VueRouter { static install(Vue) { if (VueRouter.install.installed) return VueRouter.install.installed = true _Vue = Vue _Vue.mixin({ beforeCreate() { if (this.$options.router) { _Vue.prototype.$router = this.$options.router
console.log(this.$options.router.init); this.$options.router.init() } } }) } constructor(options) { this.options = options this.routeMap = {} this.data = _Vue.observable({ current: '/' }) } createRouterMap() { this.options.routes.forEach(route => this.routeMap[route.path] = route.component) } initComponents(Vue) { Vue.component('router-link', { props: { 'to': { type: String } }, render(h) { return h('a', { attrs: { href: this.to }, on: { click: this.clickHandle } }, [this.$slots.default]) }, methods: { clickHandle(e) { history.pushState({}, "", this.to) this.$router.data.current = this.to
e.preventDefault() } } }) let self = this Vue.component('router-view', { render(h) { return h(self.routeMap[self.data.current]) } }) } init() { this.createRouterMap() this.initComponents(_Vue) this.initEvent() } initEvent() { window.addEventListener("popstate", () => { this.data.current = window.location.pathname }) } }
轉自:csdn 作者:Holyforsaken_FHC
藍藍設計( www.skdbbs.com )是一家專注而深入的界面設計公司�,為期望卓越的國內外企業提供卓越的UI界面設計、BS界面設計 �����、 cs界面設計 ����、 ipad界面設計 ��、 包裝設計 ����、 圖標定制 、 用戶體驗 ����、交互設計、 網站建設 ��、平面設計服務